Kt Kingtronics Diode
2 Sept 2011Diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices.
Today most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconductors such as germanium are sometimes used.
We kingtronics have very strong offer for diode as a ISO 9001:2008 manufacturer.
We could provide you very excellent price with good quality.
We give good support to customers, many customers highly evaluated us, they said " we never meet any problem with kingtronics products, they have extremely quality, and the delivery time always is on time Like FedEx services". So kingtronics is really your reliable supplier!
Below is our new picture for some diodes. You can see our other products by visit our website: www.kingtronics.com

- 0Commentary
- Tags:
Kt Kingtronics Rectifier diodes (large current)
26 Aug 2011Rectifier diodes (large current)
Rectifier diodes are used in power supplies to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), a process called rectification. They are also used elsewhere in circuits where a large current must pass through the diode.
All rectifier diodes are made from silicon and therefore have a forward voltage drop of 0.7V. The table shows maximum current and maximum reverse voltage for some popular rectifier diodes. The 1N4001 is suitable for most low voltage circuits with a current of less than 1A.
| Diode | Maximum Current | Maximum Reverse Voltage |
| 1N4001 | 1A | 50V |
| 1N4002 | 1A | 100V |
| 1N4007 | 1A | 1000V |
| 1N5401 | 3A | 100V |
| 1N5408 | 3A | 1000V |
- 0Commentary
- Tags:
As you know, general diode rectifier M7, 1N4007 and switching diode LL4148 are very common and popular in the market. This year, we win really good diode orders.
To support customers better, Kingtronics prepare stocks on offer. So the price and lead time are very attractive.
Pls note all the parts are NEW and Original. First come, first served. We will replenish stock once use out. Do you have any order plan now?
Stock status:
Axial Diode 1N4007 DO-41 T&R RoHS. 1,500,000pcs in stock (US$ 0.0057/pc)
SMD Diode M7 DO-214AC T&R RoHS. 550, 000pcs in stock
Switching Diode LL4148 LL-34 T&R RoHS. 2,000,000pcs in stock
Pls visit our website www.kingtronics.com for details.


- 0Commentary
- Tags:
In 1938, German scientist Walter Schottky developed a diode having a metal to semiconductor junction.
A Schottky diode, like other solid-state diodes, conducts electrical current in one direction.
It can operate at higher speeds than typical silicon diodes.
Advantages
Small pockets of electric charge build up in a typical silicon diode, slowing down its ability to turn current off.
A Schottky diode can operate hundreds of times faster since it avoids build up of electric charges.
It also has less than half the voltage drop conducting in the forward direction than a silicon diode.
Applications
Engineers use Schottky diodes in very high-frequency circuits, such as microwave transmitters.
Schottky diodes also see use in switching power supplies and solar battery charging systems.
Kingtronics produce and sell schottky diode 1N5817-1N5819, 1N5820-1N5822. if you have inquiry, pls send email to anna@kingtronics.cn.
- 0Commentary
- Tags:
Silicon diodes act as one-way valves for electrical current, allowing it to flow in only one direction. Like any electronic component,
diodes can fail from excessive voltage or current. Fortunately, diodes are simple to test, needing only a good multimeter to check them.
If you set the multimeter to read resistance and put the probes across the diode, you should read a low resistance one way and high resistance
with the probes reversed. A shorted diode will read low resistance both ways, and a blown diode will read high resistance both ways.
Instructions
1.Turn off the power to your circuit or equipment. Let the equipment sit for at least 30 minutes before removing the case or cover to allow the power supply to discharge。
2.Locate the diodes you want to test. They are typically small, two-lead parts with a stripe on the body to indicate the diode's cathode side.
3.Turn the multimeter on and turn the function knob so it points to the resistance setting. Hold the plastic body of the probes and are not touching the metal tips.
Touch the tip of the positive probe to one side of the diode and the negative probe to the other side. Read the resistance measurement and write it down.
Reverse the probes so they're touching the opposite sides of the diode. Write down the resistance you read . The higher resistance should be at least 10
times greater than the lower one. If it's less than five, the diode is very likely bad.
Kingtronics produce many types of diode rectifier,such as silicon diode, switching diodes, fast recovery diodes zener diodes.... Pls visit our updated website www.kingtronics.com for the details.
Any inquiry, pls send to anna@kingtronics.cn . Many thanks!
- 0Commentary
- Tags:
Kt Kingtronics Diodes
25 Jul 2011There are a number of different electronic devices which tend to be called diodes.
Although they're made differently they all have three things in common.
They have two leads like a resistor.
The current they pass depends upon the voltage between the leads.
They do not obey Ohm's law!
As an example we will use a typical diode called a pn-junction. This allows us to explain behaviour of diodes.
The function of a diode is to allow current in one direction and to block current in the opposite direction.
The terminals of a diode are called the anode and cathode. There are two kinds of semiconductor diodes: a P-N junction diode, which forms an electrical barrier at the interface between N- and P-type semiconductor layers, and a Schottky diode, whose barrier is formed between metal and semiconductor regions.
Remember, however, that there are other sorts of diodes which are built differently but show the same general behaviour.
Kt Kingtronics Rectifier's Application
13 Jul 2011Rectifiers find a use in detection of amplitude modulated radio signals. The signal may be amplified before detection, but if un-amplified, a very low voltage drop diode must be used. When using a rectifier for demodulation the capacitor and load resistance must be carefully matched. Too low a capacitance will result in the high frequency carrier passing to the output and too high will result in the capacitor just charging and staying charged.
Kingtronics’s fast recovery rectifier diodes are very popular in the overseas market, According to the rectifier’ s application , Our Kingtronics managing ordinary rectifier diodes, ultra-fast rectifier diodes. In our Kingtronics website www.kingtronics.com ,we have detailed PDF about all kinds of diodes & rectifiers.
- 0Commentary
- Tags:
Kt Kingtronics Uses of Zener Diodes
11 Jul 2011Since the voltage dropped across a Zener Diode is a known and fixed value, Zener diodes are typically used to regulate the voltage in electric circuits. Using a resistor to ensure that the current passing through the Zener diode is at least 5mA (0.005 Amps), the circuit designer knows that the voltage drop across the diode is exactly equal to the Zener voltage of the diode.
NEW Click here to visit Zener-Diode.co.uk for a site dedicated to zener diodes, their characteristics, usage, and other information.
Zener Diode Voltage Regulator Circuit
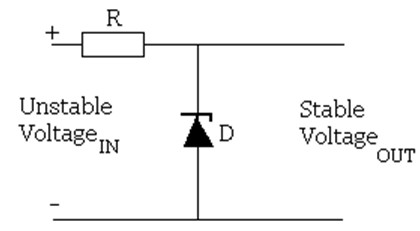
A zener diode can be used to make a simple voltage regulation circuit as pictured above. The output voltage is fixed at the zener voltage of the zener diode used and so can be used to power devices requiring a fixed voltage. Click here to find out more about the Zener Diode Voltage Regulator and how you go about selecting the resistor and zener diode.
NEW The above mentioned article on zener diode voltage regulators has now been updated and a handy calculator has been added to help you select the correct resistor and zener diode values and power ratings.
Zener Diodes in Series With Loads
If you have a regulated fixed voltage - say 12 Volts from a desktop PC power supply, and you want to power something requiring a lower voltage, it is possible to simply place a zener diode in series with the load device. You would choose a diode with a zener voltage equal to the supply voltage minus the voltage drop across the load.

For example, if you have a 1 Watt 6 Volt lightbulb to power from a 12 Watt regulated power supply, a 6.2V zener diode could be placed in series with the bulb giving the bulb 5.8V, or you could overpower the bulb a little using a 5.6V zener diode and dropping 6.4V across the bulb. Heat would be generated in the zener diode so it is essential to calculate the power lost in it so a suitably rated diode could be chosen.
Using a 5.6V zener diode, and knowing the bulb draws a current of around one-sixth of an Amp, we can calculate the power loss in the diode (with Ohm's Law) to be just under 1 Watt. Therefore a standard 1.3 Watt zener diode should be up to the job.
Circuits with Zener Diodes
Zener diodes are key components in the circuits presented in the following articles: Make a Simple Battery Status Monitor, LM741 Voltage Indicator, and High Capacity Alternative to 9V Battery.
Kt Kingtronics Zener diodes
8 Jul 2011Zener diodes are used to maintain a fixed voltage. They are designed to 'breakdown' in a reliable and non-destructive way so that they can be used in reverse to maintain a fixed voltage across their terminals.
Zener diodes can be distinguished from ordinary diodes by their code and breakdown voltage which are printed on them. Zener diode codes begin BZX... or BZY... Their breakdown voltage is printed with V in place of a decimal point, so 4V7 means 4.7V for example.
Kingtronics supplies BZV55C/ZMM55C-SERIES with Low zener impedance,Low regulation factor,Glass passivated junction,High temperature soldering guaranteed:260 C/10S at terminals. Please link http://www.kingtronics.com/pdf/BZV55C.pdf ,you will see all series of our Zener diodes.
- 0Commentary
- Tags:
Kt Kingtronics Function of diode
4 Jul 2011The most common function of a diode is to allow an electric current to pass in one direction (called the diode's forward direction) while blocking current in the opposite direction (the reverse direction). Thus, the diode can be thought of as an electronic version of a check valve. This unidirectional behavior is called rectification, and is used to convert alternating current to direct current, and to extract modulation from radio signals in radio receivers.
Different types of diode will have different function, this is depends on their voltage, temperature, and other factor. So it is very important when you check your diode, Our Kingtronics provide diode's detailed function. If you have any problems, please look for some suggestions in www.kingtronics.com.
- 0Commentary
- Tags:
Contact us
Tel: (86) 769 8118 8110
Tel: (852) 8106 7033
Fax: (852) 8106 7099
E-mail: info@kingtronics.com
Microsoft Teams: Kingtronics.sales via Teams
WhatsApp: Chat with us on WhatsApp
Web: www.Kingtronics.com
YouTube: www.youtube.com/c/Kingtronicskt
About
Kingtronics International Company was established in 1995 located in Dongguan City of China to handle all sales & marketing for factories located in Chengdu, Sichuan and Zhaoqing, Guangdong, China. In 1990, we established the first factory to produce trimming potentiometer and in 1999 we built up new factory in Zhao Qing, Guangdong. Now with around 850 workers, Kingtronics produce trimming potentiometers, dipped tantalum capacitors, multilayer ceramic capacitors, and diode & bridge rectifier. We sell good quality under our brand Kingtronics, and Kt, King, Kingtronics are our three trademarks. All our products are RoHS compliant, and our bridge rectifier have UL approval. Please visit our Products page, you could please download all our PDF datasheet and find cross reference for our Trimming Potentiometer and capacitors.
Tantalum and Ceramic Capacitors Cross Reference ↓ Download
Diodes & Rectifiers List(PDF: 97KB) ↓ Download
Trimming Potentiometer Cross Reference ↓Download
Categories
- Kt Kingtronics (252)
- Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor (165)
- Diodes & Rectifiers (162)
- Trimming Potentiometers (130)
- Tantalum Capacitors (96)
- Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors (70)
- Kt Bridge Rectifier (66)
- Quartz Crystals (64)
- Film Capacitors (43)
- Surge Arresters (34)
- Tactile Switches (34)
- Kt Kingtronics Components (31)
- Ceramic Trimmer Capacitors (27)
- Super Capacitors (22)
- Metal Oxide Varistor (13)
- Negative Temperature Coefficient Thermistor (6)
- Special Purpose Film Capacitors (3)
- Music capacitors (2)
- Resistors (1)
- LED Display Modules (1)
Archives
- 2026 February (2)
- 2026 January (2)
- 2025 December (3)
- 2025 November (2)
- 2025 October (2)
- 2025 September (4)
- 2025 August (4)
- 2025 July (4)
- 2025 June (6)
- 2025 May (4)
- 2025 April (3)
- 2025 March (3)
- 2025 February (3)
- 2025 January (4)
- 2024 December (2)
- 2024 November (5)
- 2024 October (4)
- 2024 September (6)
- 2024 August (9)
- 2024 July (6)
- 2024 June (5)
- 2024 May (3)
- 2024 April (3)
- 2024 March (2)
- 2024 February (2)
- 2024 January (3)
- 2023 December (1)
- 2023 November (2)
- 2023 October (1)
- 2023 September (2)
- 2023 August (2)
- 2023 July (4)
- 2023 June (12)
- 2023 May (6)
- 2023 April (4)
- 2023 March (3)
- 2023 February (2)
- 2023 January (1)
- 2022 December (3)
- 2022 November (2)
- 2022 October (3)
- 2022 September (4)
- 2022 August (3)
- 2022 July (3)
- 2022 June (2)
- 2022 May (3)
- 2022 April (4)
- 2022 March (4)
- 2022 February (2)
- 2022 January (3)
- 2021 December (4)
- 2021 November (3)
- 2021 October (4)
- 2021 September (4)
- 2021 August (4)
- 2021 July (4)
- 2021 June (5)
- 2021 May (4)
- 2021 April (3)
- 2021 March (4)
- 2021 February (4)
- 2021 January (4)
- 2020 December (5)
- 2020 November (4)
- 2020 October (4)
- 2020 September (7)
- 2020 August (8)
- 2020 July (9)
- 2020 June (8)
- 2020 May (9)
- 2020 April (11)
- 2020 March (6)
- 2020 February (4)
- 2020 January (4)
- 2019 December (6)
- 2019 November (7)
- 2019 October (6)
- 2019 September (5)
- 2019 August (9)
- 2019 July (6)
- 2019 June (4)
- 2019 May (16)
- 2019 April (6)
- 2019 March (6)
- 2019 February (9)
- 2019 January (5)
- 2018 December (4)
- 2018 November (4)
- 2018 October (5)
- 2018 September (8)
- 2018 August (10)
- 2018 July (7)
- 2018 June (12)
- 2018 May (22)
- 2018 April (4)
- 2018 March (4)
- 2018 February (8)
- 2018 January (13)
- 2017 December (4)
- 2017 November (4)
- 2017 October (5)
- 2017 September (4)
- 2017 August (20)
- 2017 July (7)
- 2017 June (5)
- 2017 May (4)
- 2017 April (4)
- 2017 March (8)
- 2017 February (8)
- 2017 January (8)
- 2016 December (10)
- 2016 November (16)
- 2016 October (8)
- 2016 September (10)
- 2016 August (13)
- 2016 July (12)
- 2016 June (10)
- 2016 May (14)
- 2016 April (8)
- 2016 March (10)
- 2016 February (6)
- 2016 January (8)
- 2015 December (10)
- 2015 November (8)
- 2015 October (3)
- 2015 July (5)
- 2015 June (9)
- 2015 May (7)
- 2015 April (8)
- 2015 March (9)
- 2015 February (7)
- 2015 January (5)
- 2014 December (13)
- 2014 November (4)
- 2014 October (4)
- 2014 September (5)
- 2014 August (4)
- 2014 July (4)
- 2014 June (4)
- 2014 May (4)
- 2014 April (4)
- 2014 March (5)
- 2014 February (3)
- 2014 January (4)
- 2013 December (8)
- 2013 November (9)
- 2013 October (10)
- 2013 September (9)
- 2013 August (11)
- 2013 July (10)
- 2013 June (3)
- 2013 May (4)
- 2013 April (3)
- 2013 March (2)
- 2013 February (1)
- 2013 January (3)
- 2012 December (5)
- 2012 November (6)
- 2012 October (5)
- 2012 September (10)
- 2012 August (11)
- 2012 July (11)
- 2012 June (12)
- 2012 May (14)
- 2012 April (9)
- 2012 March (14)
- 2012 February (9)
- 2012 January (6)
- 2011 December (9)
- 2011 November (11)
- 2011 October (10)
- 2011 September (13)
- 2011 August (14)
- 2011 July (13)
- 2011 June (13)
- 2011 May (13)
- 2011 April (14)
- 2011 March (27)
- 2011 February (13)
- 2011 January (24)
- 2010 December (21)
- 2010 November (12)
- 2010 October (11)

