Kt Kingtronics Diode Bridge Rectifier
21 Mar 2011A diode bridge is an arrangement of four (or more) diodes in a bridge configuration that provides the same polarity of output for either polarity of input. When used in its most common application, for conversion of an alternating current (AC) input into direct current a (DC) output, it is known as a bridge rectifier. A bridge rectifier provides full-wave rectification from a two-wire AC input, resulting in lower cost and weight as compared to a rectifier with a 3-wire input from a transformer with a center-tapped secondary winding.
The essential feature of a diode bridge is that the polarity of the output is the same regardless of the polarity at the input. The diode bridge circuit is also known as the Graetz circuit after its inventor, physicist Leo Graetz.
In actuality, free electrons in a conductor nearly always flow from the negative to the positive pole. In the vast majority of applications, however, the actual direction of current flow is irrelevant. Therefore, in the discussion below the conventional model is retained.
Prior to the availability of integrated circuits, a bridge rectifier was constructed from "discrete components", i.e., separate diodes. Since about 1950, a single four-terminal component containing the four diodes connected in a bridge configuration became a standard commercial component and is now available with various voltage and current ratings.
For many applications, especially with single phase AC where the full-wave bridge serves to convert an AC input into a DC output, the addition of a capacitor may be desired because the bridge alone supplies an output of fixed polarity but continuously varying or "pulsating" magnitude, an attribute commonly referred to as "ripple".
- 0Commentary
- Tags:
Schottky Rectifiers have been used in the power supply industry for approximately 15 years. During this time, significant fiction as well as fact has been associated with this type of rectifier. The primary assets of Schottky devices are switching speeds approaching zero-time and very low forward voltage drop (VF). This combination makes Schottky barrier rectifiers ideal for the output stages of switching power supplies. On the negative side, Schottky devices are also known for limited high-temperature operation, high eakage and limited voltage range BVR. Though these limitations exist, they are quantifiable and controllable, allowing wide application of these devices in switch mode power supplies.
- 0Commentary
- Tags:
Kingtronics Zener Diodes Function
16 Mar 2011Zener diodes regulate voltage by acting as complementary loads, drawing more or less current as necessary to ensure a constant voltage drop across the load. This is analogous to regulating the speed of an automobile by braking rather than by varying the throttle position: not only is it wasteful, but the brakes must be built to handle all the engine's power when the driving conditions don't demand it. Despite this fundamental inefficiency of design, zener diode regulator circuits are widely employed due to their sheer simplicity. In high-power applications where the inefficiencies would be unacceptable, other voltage-regulating techniques are applied. But even then, small zener-based circuits are often used to provide a “reference” voltage to drive a more efficient amplifier circuit controlling the main power.
- 0Commentary
- Tags:
Kingtronics Half-wave Rectifier Circuit
10 Mar 2011For most power application, half-wave rectification is insufficient for the task. The harmonic content of the rectifier’s output waveform is very large and consequently difficult to filter. Furthermore, the AC power source only supplies power to the load one half every full cycle, meaning that half of its capacity is unused. Half-wave rectification is, however, a very simple way to reduce power to a resistive load. Some two position lamp dimmer switches apply full AC power to the lamp filament for “full” brightness and then half-wave rectify it for a lesser light output.
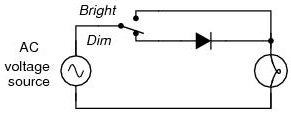
- 0Commentary
- Tags:
One advantage of remembering this layout for a bridge rectifier circuit is that it expands easily into a polyphase version in Figure below
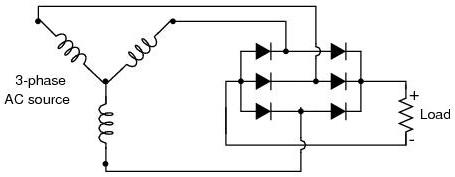
- 0Commentary
- Tags:
Despite the fact that Schottky barrier diodes have many applications in today's high tech electronics scene, it is actually one of the oldest semiconductor devices in existence. As a metal-semiconductor devices, its applications can be traced back to before 1900 where crystal detectors, cat's whisker detectors and the like were all effectively Schottky barrier diodes.
The Schottky diode symbol used in many circuit schematic diagrams may be that of an ordinary diode symbol. However it is often necessary to use a specific Schottky diode symbol to signify that a Schottky diode rather than another one must be used because it is essential to the operation of the circuit. Accordingly a specific Schottky diode symbol has been accepted for use. This Schottky diode symbol is shown below:
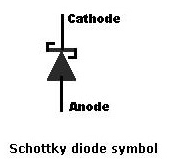

Kingtronics Kt Schottky Rectifiers
9 Feb 2011Schottky rectifiers have been used in the power supply industry for approximately 15 years. During this time, significant fiction as well as fact has been associated with this type of rectifier. The primary assets of Schottky devices are switching speeds approaching zero-time and very low forward voltage drop (VF). This combination makes Schottky barrier rectifiers ideal for the output stages of switching power supplies. On the negative side, Schottky devices are also known for limited high-temperature operation, high leakage and limited voltage range BVR. Though these limitations exist, they are quantifiable and controllable, allowing wide application of these devices in switch mode power supplies.
High leakage, when associated with standard P-N junction rectifiers, usually indicates “badness,” implying poor reliability. In a Schottky device, leakage at high temperature(75 °C and greater) is often on the order to several milliamps, depending on chip size. In the case of Schottky barrier rectifiers, high-temperature leakage and forward voltage drop are controlled by two primary factors: the size of the chip’s active area and the barrier height (φB).
- 0Commentary
- Tags:
Reverse Voltage - 20 to 40 Volts Forward Current - 3.0 Amperes
FEATURES
- Plastic package has Underwriters Laboratory Flammability Classification 94V-0
- Metal silicon junction, majority carrier conduction
- Guardring for over voltage protection
- Low power loss, high erriciency
- High current capability, low forward voltage drop
- High surge capability
- For use in low voltage, high frequency inverters, free wheeling, and polarity protection applications
- High temperature soldering guaranteed:
250℃ /10 seconds, 0.375”(9.5mm) lead length,5 lbs. (2.3kg) tension
- 0Commentary
- Tags:
Kt Kingtronics Bridge Rectifier Full List
18 Jan 2011Diode have many types: ordinary rectifier diodes, ultra-fast rectifier diodes, transient voltage suppression diodes, switching diodes, high voltage diodes, diode bridge rectifier, SMT surface mount fast recovery diodes, surface-mount schottky diodes SMD, fast recovery rectifier diodes, schottky diodes, bi-directional trigger diodes, zener diodes,damping diodes, ordinary surface mount diodes SMT, SMT surface mount ultra-fast diodes, TO-220 packaged diodes, power snubber diode, etc.
Below are Kingtronics bridge rectifier full list, do you buy any of these? Kindly send your inquiry to info@kingtronics.com
Welcome to check our price!
Kingtronics team
| No. | Type | Package | Packing |
| ABS | ABS2-ABS6 | ABS | Tape & Reel |
| ABS8 | ABS | Tape & Reel | |
| ABS10 | ABS | Tape & Reel | |
| MBS | MB1S-MB6S | MBS | Tape & Reel |
| MB8S | MBS | Tape & Reel | |
| MB10S | MBS | Tape & Reel | |
| MBM | MB1M-MB6M | MBM | Tube |
| MB8M | MBM | Tube | |
| MB10M | MBM | Tube | |
| DB | DB101-DB105 | DB | Tube |
| DB106-DB107 | DB | Tube | |
| DB151-DB155 | DB | Tube | |
| DB156-DB157 | DB | Tube | |
| DBS | DB101S-DB105S | DBS | Tube |
| DB106S-DB107S | DBS | Tube | |
| DB151S-DB155S | DBS | Tube | |
| DB156S-DB157S | DBS | Tube | |
| KBP | KBP2005-KBP06 | KBP | Bulk |
| KBP08-KBP210 | KBP | Bulk | |
| KBP3005-KBP06 | KBP | Bulk | |
| KBP308-KBP310 | KBP | Bulk | |
| GBP | GBP2005-GBP210 | GBP | Bulk |
| GBP3005-GBP310 | GBP | Bulk | |
| KBL | KBL401-KBL406(RS401L-RS406L) | KBL | Bulk |
| KBL08-KBL410 | KBL | Bulk | |
| KBL601-KBL608(RS601L-RS606L) | KBL | Bulk | |
| KBL610 | KBL | Bulk | |
| KBU | KBU4005-KBU406(RS4) | KBU | Bulk |
| KBU408-KBU410(RS4) | KBU | Bulk | |
| KBU6005-KBU606(RS6) | KBU | Bulk | |
| KBU608-KBU610(RS6) | KBU | Bulk | |
| KBU8005-KBU806(RS8) | KBU | Bulk | |
| KBU808-KBU810(RS8) | KBU | Bulk | |
| KBU10005-KBU1006 | KBU | Bulk | |
| KBU1008-KBU1010 | KBU | Bulk | |
| KBU15005-KBU1506 | KBU | Bulk | |
| KBU1508-KBU1510 | KBU | Bulk | |
| KBU25005-KBU2506 | KBU | Bulk | |
| KBU25008-KBU2510 | KBU | Bulk | |
| KBU35005-KBU3506 | KBU | Bulk | |
| KBU3508-KBU3510 | KBU | Bulk | |
| GBU | GBU4005-GBU406 | GBU | Bulk |
| GBU408-GBU410 | GBU | Bulk | |
| GBU6005-GBU606 | GBU | Bulk | |
| GBU608-GBU610 | GBU | Bulk | |
| GBU8005-GBU806 | GBU | Bulk | |
| GBU808-GBU810 | GBU | Bulk | |
| GBU10005-GBU1006 | GBU | Bulk | |
| GBU1008-GBU1010 | GBU | Bulk | |
| GBU15005-GBU1510 | GBU | Bulk | |
| GBU20005-GBU2010 | GBU | Bulk | |
| GBU25005-GBU2510 | GBU | Bulk | |
| KBJ4(3S) | KBJ4005-KBJ406 | KBJ4(3S) | Bulk |
| KBJ408-KBJ410 | KBJ4(3S) | Bulk | |
| KBJ6005-KBJ606 | KBJ4(3S) | Bulk | |
| KBJ608-KBJ610 | KBJ4(3S) | Bulk | |
| KBJ8005-KBJ806 | KBJ4(3S) | Bulk | |
| KBJ808-KBJ810 | KBJ4(3S) | Bulk | |
| KBJ10005-KBJ1006 | KBJ4(3S) | Bulk | |
| KBJ1008-KBJ1010 | KBJ4(3S) | Bulk | |
| KBJ15005-KBJ1506 | KBJ4(3S) | Bulk | |
| KBJ1508-KBJ1510 | KBJ4(3S) | Bulk | |
| KBJ6(5S) | GBJ6005-GBJ606 | KBJ6(5S) | Bulk |
| GBJ608-GBJ610 | KBJ6(5S) | Bulk | |
| GBJ8005-GBJ806 | KBJ6(5S) | Bulk | |
| GBJ808-GBJ810 | KBJ6(5S) | Bulk | |
| GBJ10005-GBJ1006 | KBJ6(5S) | Bulk | |
| GBJ1008-GBJ1010 | KBJ6(5S) | Bulk | |
| GBJ15005-GBJ1506 | KBJ6(5S) | Bulk | |
| GBJ1508-GBJ1510 | KBJ6(5S) | Bulk | |
| GBJ20005-GBJ2006 | KBJ6(5S) | Bulk | |
| GBJ2008-GBJ2010 | KBJ6(5S) | Bulk | |
| GBJ25005-GBJ2506 | KBJ6(5S) | Bulk | |
| GBJ2508-GBJ2510 | KBJ6(5S) | Bulk | |
| GBJ35005-GBJ3506 | KBJ6(5S) | Bulk | |
| GBJ3508-GBJ3510 | KBJ6(5S) | Bulk | |
| KBPC1 | KBPC1005-KBPC106 | KBPC1 | Bulk |
| KBPC108-KBPC110 | KBPC1 | Bulk | |
| KBPC6 | KBPC6005-KBPC6006 | KBPC6 | Bulk |
| KBPC608-KBPC610 | KBPC6 | Bulk | |
| KBPC6005-KBPC6006 | KBPC6 | Bulk | |
| KBPC608-KBPC610 | KBPC6 | Bulk | |
| KBPC8 | KBPC8005-KBPC806 | KBPC8 | Bulk |
| KBPC808-KBPC810 | KBPC8 | Bulk | |
| KBPC8005L-KBPC806L | KBPC8 | Bulk | |
| KBPC808L-KBPC810L | KBPC8 | Bulk | |
| KBPC10005-KBPC1006 | KBPC8 | Bulk | |
| KBPC1008-KBPC1010 | KBPC8 | Bulk | |
| KBPC10005L-KBPC1006L | KBPC8 | Bulk | |
| KBPC1008L-KBPC1010L | KBPC8 | Bulk | |
| KBPC/ KBPC-W | KBPC15005-KBPC1506 | KBPC/ KBPC-W | Bulk |
| KBPC1508-KBPC1510 | KBPC/ KBPC-W | Bulk | |
| KBPC25005-KBPC2506 | KBPC/ KBPC-W | Bulk | |
| KBPC2508-KBPC2510 | KBPC/ KBPC-W | Bulk | |
| KBPC35005-KBPC3506 | KBPC/ KBPC-W | Bulk | |
| KBPC3508-KBPC3510 | KBPC/ KBPC-W | Bulk | |
| KBPC50005-KBPC5006 | KBPC/ KBPC-W | Bulk | |
| KBPC5008-KBPC5010 | KBPC/ KBPC-W | Bulk | |
| BR/BR-W | BR15005-BR1506 | BR/BR-W | Bulk |
| BR15008-BR1510 | BR/BR-W | Bulk | |
| BR25005-BR2506 | BR/BR-W | Bulk | |
| BR25008-BR2510 | BR/BR-W | Bulk | |
| BR35005-BR3506 | BR/BR-W | Bulk | |
| BR35008-BR3510 | BR/BR-W | Bulk | |
| BR50005-BR5006 | BR/BR-W | Bulk | |
| BR50008-BR5010 | BR/BR-W | Bulk | |
| BR-L | BR15005L-BR1506L | BR-L | Bulk |
| BR15008L-BR1510L | BR-L | Bulk | |
| BR25005L-BR2506L | BR-L | Bulk | |
| BR25008L-BR2510L | BR-L | Bulk | |
| BR35005L-BR3506L | BR-L | Bulk | |
| BR35008L-BR3510L | BR-L | Bulk | |
| BR50005L-BR5006L | BR-L | Bulk | |
| BR50008L-BR5010L | BR-L | Bulk | |
| GBPC | GBPC15005-GBPC1506 | GBPC | Bulk |
| GBPC15008-GBPC1510 | GBPC | Bulk | |
| GBPC25005-GBPC2506 | GBPC | Bulk | |
| GBPC25008-GBPC2510 | GBPC | Bulk | |
| GBPC35005-GBPC3506 | GBPC | Bulk | |
| GBPC35008-GBPC3510 | GBPC | Bulk | |
| GBPC50005-GBPC5006 | GBPC | Bulk | |
| GBPC50008-GBPC5010 | GBPC | Bulk | |
| GBPCW | GBPC15005-GBPC1510W | GBPCW | Bulk |
| GBPC25005-GBPC2510W | GBPCW | Bulk | |
| GBPC35005-GBPC3510W | GBPCW | Bulk | |
| GBPC50005-GBPC5010W | GBPCW | Bulk | |
| SKBPC | SKBPC2501-SKBPC2510 | SKBPC | Bulk |
| SKBPC2512-SKBPC2516 | SKBPC | Bulk | |
| SKBPC3501-SKBPC3510 | SKBPC | Bulk | |
| SKBPC3512-SKBPC3516 | SKBPC | Bulk | |
| SKBPC5001-SKBPC5010 | SKBPC | Bulk | |
| SKBPC5012-SKBPC5016 | SKBPC | Bulk |

A Zener Diode is a special kind of diode which permits current to flow in the forward direction as normal, but will also allow it to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage is above a certain value - the breakdown voltage known as the Zener voltage.
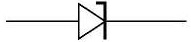
The Zener voltage of a standard diode is high, but if a reverse current above that value is allowed to pass through it, the diode is permanently damaged. Zener diodes are designed so that their Zener voltage is much lower - for example just 2.4 Volts. When a reverse current above the Zener voltage passes through a Zener diode, there is a controlled breakdown which does not damage the diode. The voltage drop across the Zener diode is equal to the Zener voltage of that diode no matter how high the reverse bias voltage is above the Zener voltage.
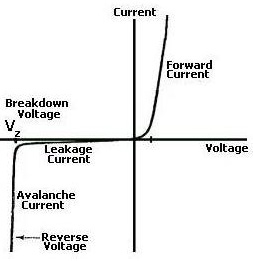
The illustration above shows this phenomenon in a Current vs. Voltage graph. With a Zener diode connected in the forward direction, it behaves exactly the same as a standard diode - i.e. a small voltage drop of 0.3 to 0.7V with current flowing through pretty much unrestricted. In the reverse direction however there is a very small leakage current between 0V and the Zener voltage - i.e. just a tiny amount of current is able to flow. Then, when the voltage reaches the breakdown voltage (Vz), suddenly current can flow freely through it.
Uses of Zener Diodes
Since the voltage dropped across a Zener Diode is a known and fixed value, Zener diodes are typically used to regulate the voltage in electric circuits. Using a resistor to ensure that the current passing through the Zener diode is at least 5mA (0.005 Amps), the circuit designer knows that the voltage drop across the diode is exactly equal to the Zener voltage of the diode.
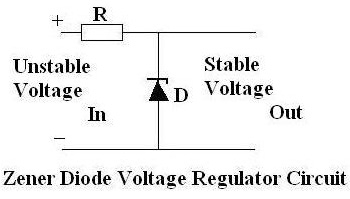
A Zener diode can be used to make a simple voltage regulation circuit as pictured above. The output voltage is fixed at the Zener voltage of the Zener diode used and so can be used to power devices requiring a fixed voltage.
If you have any inquiry about Zener diode, pls contact info@kingtronics.com
- 0Commentary
- Tags:
Contact us
Tel: (86) 769 8118 8110
Tel: (852) 8106 7033
Fax: (852) 8106 7099
E-mail: info@kingtronics.com
Skype: kingtronics.sales
Web: www.Kingtronics.com
YouTube: www.youtube.com/c/Kingtronicskt
About
Kingtronics International Company was established in 1995 located in Dongguan City of China to handle all sales & marketing for factories located in Chengdu, Sichuan and Zhaoqing, Guangdong, China. In 1990, we established the first factory to produce trimming potentiometer and in 1999 we built up new factory in Zhao Qing, Guangdong. Now with around 850 workers, Kingtronics produce trimming potentiometers, dipped tantalum capacitors, multilayer ceramic capacitors, and diode & bridge rectifier. We sell good quality under our brand Kingtronics, and Kt, King, Kingtronics are our three trademarks. All our products are RoHS compliant, and our bridge rectifier have UL approval. Please visit our Products page, you could please download all our PDF datasheet and find cross reference for our Trimming Potentiometer and capacitors.
Tantalum and Ceramic Capacitors Cross Reference ↓ Download
Diodes & Rectifiers List(PDF: 97KB) ↓ Download
Trimming Potentiometer Cross Reference ↓Download
Categories
- Kt Kingtronics (245)
- Diodes & Rectifiers (161)
- Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor (161)
- Trimming Potentiometers (128)
- Tantalum Capacitors (96)
- Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors (70)
- Quartz Crystals (64)
- Kt Bridge Rectifier (64)
- Surge Arresters (34)
- Film Capacitors (34)
- Tactile Switches (32)
- Kt Kingtronics Components (30)
- Ceramic Trimmer Capacitors (26)
- Super Capacitors (18)
- Metal Oxide Varistor (12)
- Negative Temperature Coefficient Thermistor (6)
- Special Purpose Film Capacitors (3)
- Music capacitors (2)
Archives
- 2025 March (3)
- 2025 February (3)
- 2025 January (4)
- 2024 December (2)
- 2024 November (5)
- 2024 October (4)
- 2024 September (6)
- 2024 August (9)
- 2024 July (6)
- 2024 June (5)
- 2024 May (3)
- 2024 April (3)
- 2024 March (2)
- 2024 February (2)
- 2024 January (3)
- 2023 December (1)
- 2023 November (2)
- 2023 October (1)
- 2023 September (2)
- 2023 August (2)
- 2023 July (4)
- 2023 June (12)
- 2023 May (6)
- 2023 April (4)
- 2023 March (3)
- 2023 February (2)
- 2023 January (1)
- 2022 December (3)
- 2022 November (2)
- 2022 October (3)
- 2022 September (4)
- 2022 August (3)
- 2022 July (3)
- 2022 June (2)
- 2022 May (3)
- 2022 April (4)
- 2022 March (4)
- 2022 February (2)
- 2022 January (3)
- 2021 December (4)
- 2021 November (3)
- 2021 October (4)
- 2021 September (4)
- 2021 August (4)
- 2021 July (4)
- 2021 June (5)
- 2021 May (4)
- 2021 April (3)
- 2021 March (4)
- 2021 February (4)
- 2021 January (4)
- 2020 December (5)
- 2020 November (4)
- 2020 October (4)
- 2020 September (7)
- 2020 August (8)
- 2020 July (9)
- 2020 June (8)
- 2020 May (9)
- 2020 April (11)
- 2020 March (6)
- 2020 February (4)
- 2020 January (4)
- 2019 December (6)
- 2019 November (7)
- 2019 October (6)
- 2019 September (5)
- 2019 August (9)
- 2019 July (6)
- 2019 June (4)
- 2019 May (16)
- 2019 April (6)
- 2019 March (6)
- 2019 February (9)
- 2019 January (5)
- 2018 December (4)
- 2018 November (4)
- 2018 October (5)
- 2018 September (8)
- 2018 August (10)
- 2018 July (7)
- 2018 June (12)
- 2018 May (22)
- 2018 April (4)
- 2018 March (4)
- 2018 February (8)
- 2018 January (13)
- 2017 December (4)
- 2017 November (4)
- 2017 October (5)
- 2017 September (4)
- 2017 August (20)
- 2017 July (7)
- 2017 June (5)
- 2017 May (4)
- 2017 April (4)
- 2017 March (8)
- 2017 February (8)
- 2017 January (8)
- 2016 December (10)
- 2016 November (16)
- 2016 October (8)
- 2016 September (10)
- 2016 August (13)
- 2016 July (12)
- 2016 June (10)
- 2016 May (14)
- 2016 April (8)
- 2016 March (10)
- 2016 February (6)
- 2016 January (8)
- 2015 December (10)
- 2015 November (8)
- 2015 October (3)
- 2015 July (5)
- 2015 June (9)
- 2015 May (7)
- 2015 April (8)
- 2015 March (9)
- 2015 February (7)
- 2015 January (5)
- 2014 December (13)
- 2014 November (4)
- 2014 October (4)
- 2014 September (5)
- 2014 August (4)
- 2014 July (4)
- 2014 June (4)
- 2014 May (4)
- 2014 April (4)
- 2014 March (5)
- 2014 February (3)
- 2014 January (4)
- 2013 December (8)
- 2013 November (9)
- 2013 October (10)
- 2013 September (9)
- 2013 August (11)
- 2013 July (10)
- 2013 June (3)
- 2013 May (4)
- 2013 April (3)
- 2013 March (2)
- 2013 February (1)
- 2013 January (3)
- 2012 December (5)
- 2012 November (6)
- 2012 October (5)
- 2012 September (10)
- 2012 August (11)
- 2012 July (11)
- 2012 June (12)
- 2012 May (14)
- 2012 April (9)
- 2012 March (14)
- 2012 February (9)
- 2012 January (6)
- 2011 December (9)
- 2011 November (11)
- 2011 October (10)
- 2011 September (13)
- 2011 August (14)
- 2011 July (13)
- 2011 June (13)
- 2011 May (13)
- 2011 April (14)
- 2011 March (27)
- 2011 February (13)
- 2011 January (24)
- 2010 December (21)
- 2010 November (12)
- 2010 October (11)
